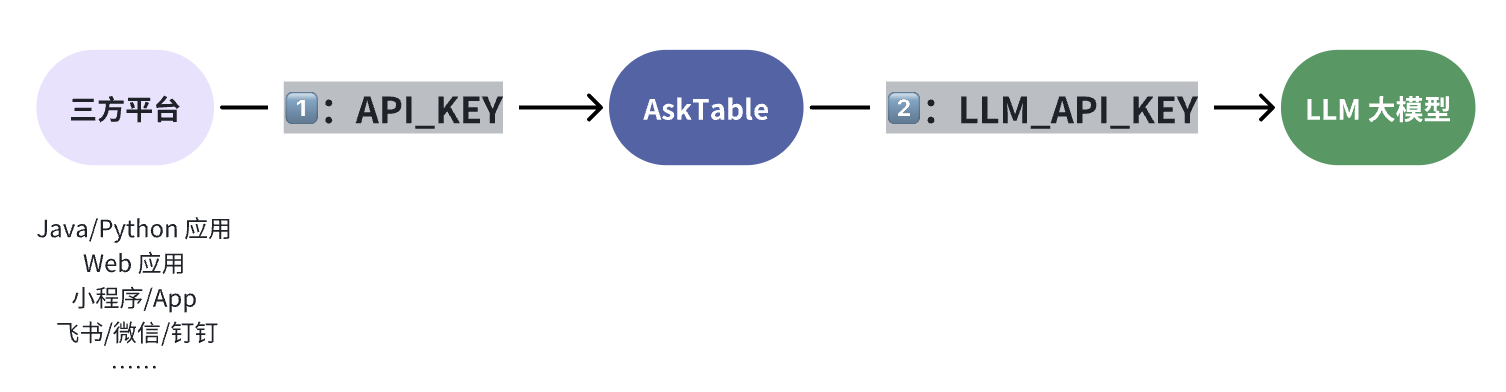
Two Types of API Keys
In AskTable, there are two types of API keys: API_KEY and LLM_API_KEY. They have different purposes and use cases. Please choose and configure them according to your actual needs.
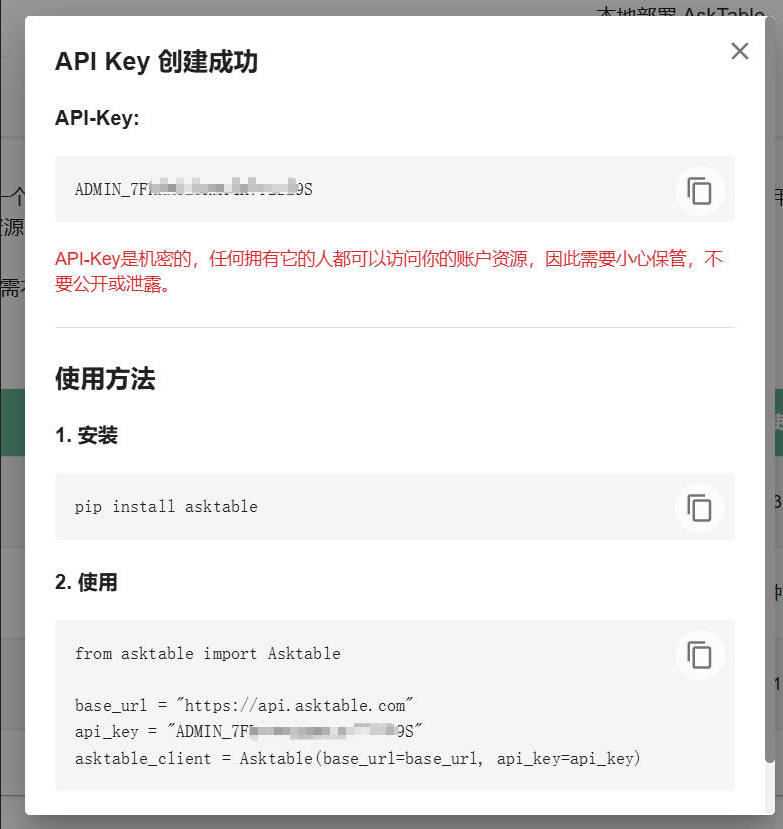
1. API_KEY
Purpose
Used to call the AskTable backend API, mainly for third-party platforms such as Feishu, Kouzi, or programs you write yourself.
Features
- Starts with
ADMIN_orASKER_, for example:ADMIN_JDML38AGS4WKPZLSYPEEASKER_JDML38AGS4WKPZLSYPEE
- Different prefixes represent different permissions. For detailed explanations, please refer to: Authentication and Authorization.
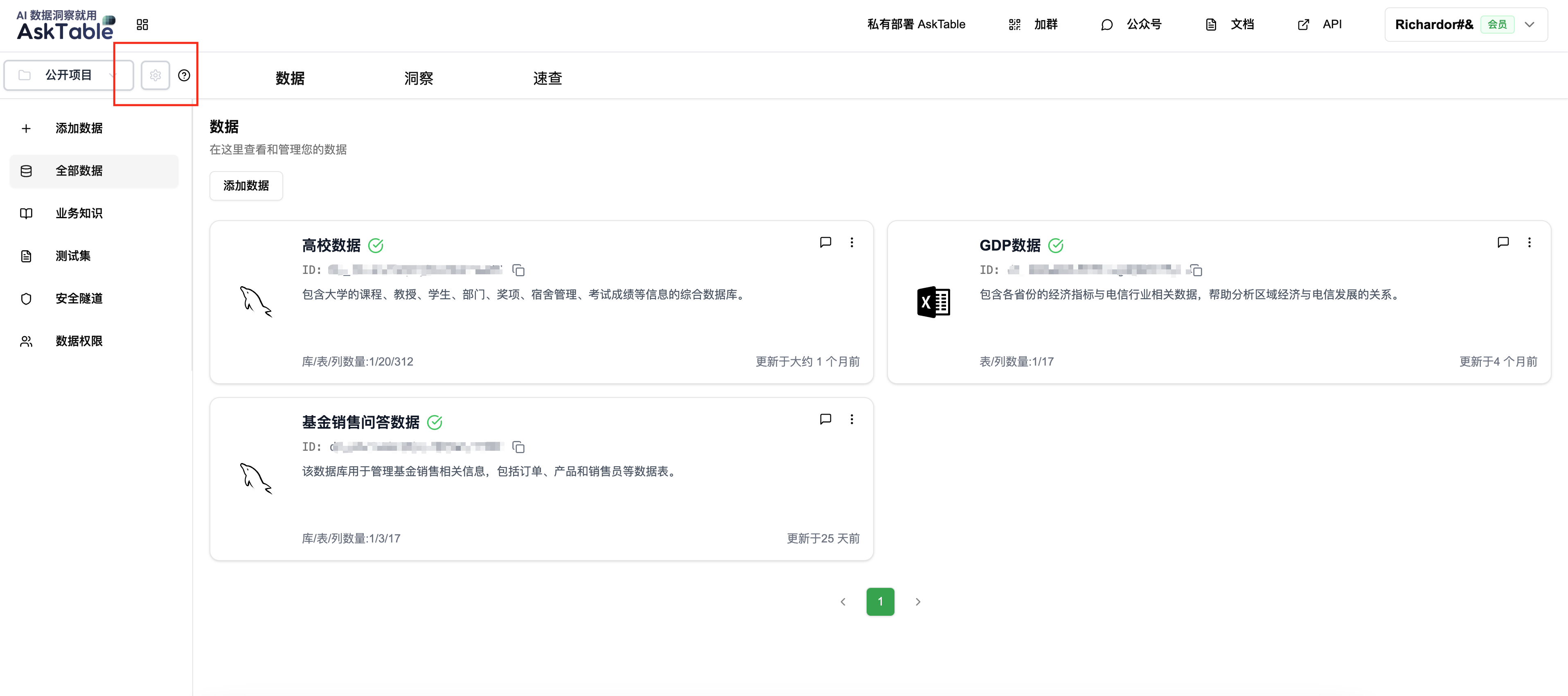
Steps to Obtain
- Enter project settings: In the AskTable main interface, find the project (e.g., "Public Project") and click the settings button (⚙️) on the right side.
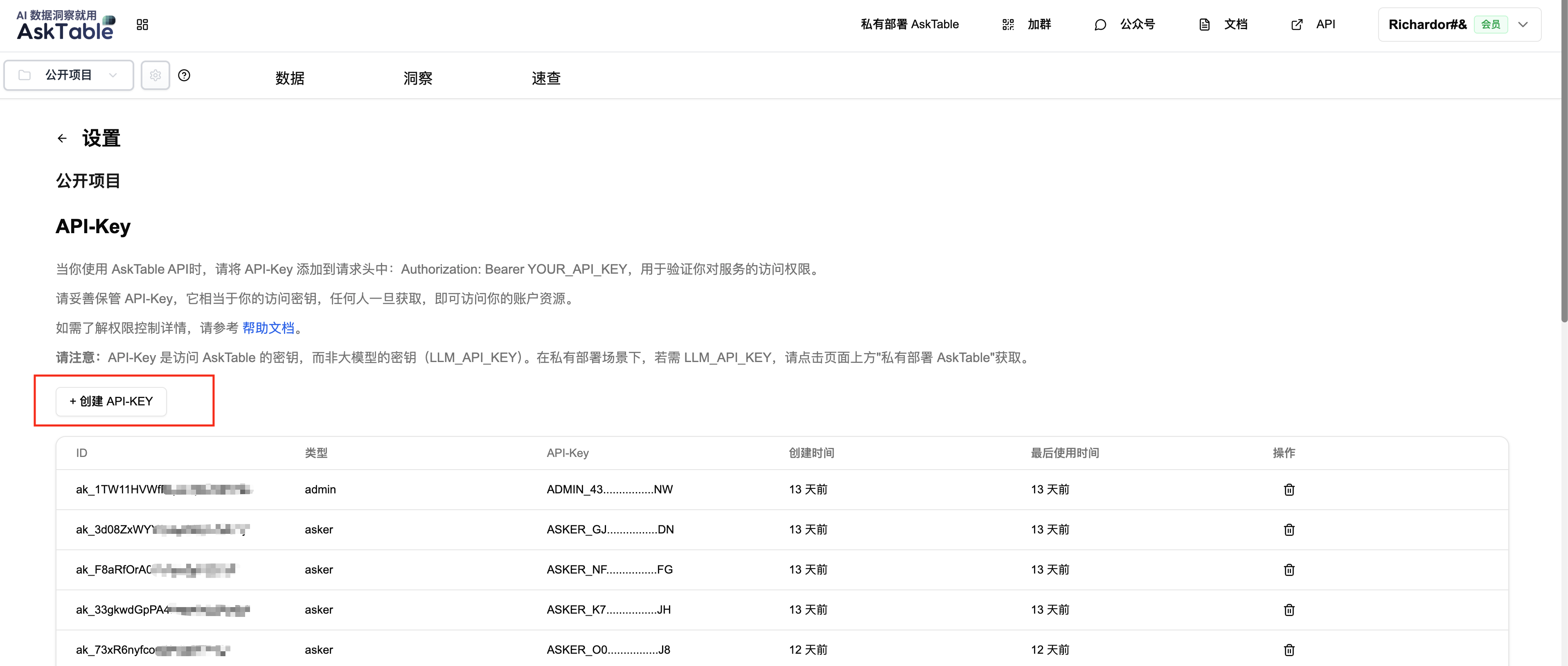
- Create a new API-Key: Go to the "API-Key" management in the left menu and click "+ New API-Key".
2. LLM_API_KEY
Purpose
Used to call cloud-based large models (such as DeepSeek, etc.). In the private deployment solution, the system needs this key to access the cloud model to ensure full functionality.
Features
- Starts with
asktable-, for example:asktable-9gwtWZUo1f319A2tGh4GQ1=.....
- It is written into the
docker-compose.ymlconfiguration file via environment variables, with the key nameLLM_API_KEY.
Configuration Steps
- Enter private deployment configuration: Click the "Private Deployment" button at the top of the AskTable main interface.
- Configure LLM_API_KEY: In the pop-up window, find "Compute Power → Configure AI Model Token" and apply for or find the LLM_API_KEY.
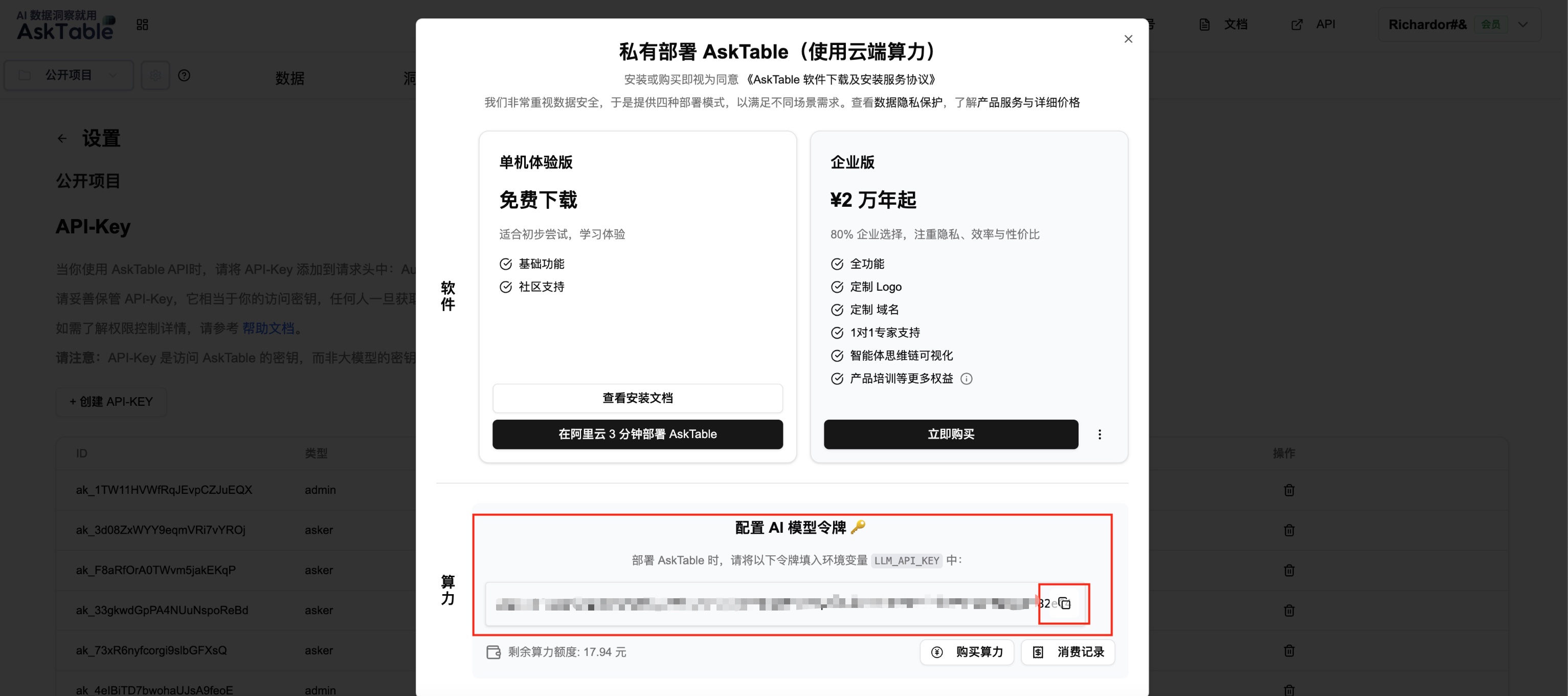
Summary: How to Distinguish These Two Types of Keys?
| Key Type | Purpose | Prefix Example | Common Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| API_KEY | Call AskTable API | ADMIN_ / ASKER_ | Integration with Feishu, Kouzi, third-party applications |
| LLM_API_KEY | Call large models (e.g., DeepSeek) | asktable- | Private deployment solutions, accessing cloud or local compute power |
Note: If connecting to a local large model, set LLM_API_KEY and LLM_BASE_URL to the parameters of your private large model service. Refer to Using a Local LLM Model.