AI Search
Feature Overview:
This feature is designed to help AskTable AI understand user inquiries and match keywords in those inquiries with data in your database.
Its core purpose is: by creating an “AI Search Index” for specific fields in the database, AskTable AI can more intelligently recognize and match user questions, providing more precise answers.
What can AI Search do?
-
Help AskTable quickly locate data fields related to a question.
For example, if a user’s question is “Datou & You performance in March,” AI Search will help AskTable locate the term “Datou & You,” which could appear in the “Company Name” field of the “Revenue Table.” Although the user’s question does not explicitly mention words like “company” or “revenue,” AskTable knows where to search for the data. -
Help AskTable generate the correct query statements.
In the previous example, “Datou & You” is not the full official company name stored in the database. If AskTable only uses “Datou & You” as the filter condition, it would not find the data. AI Search assists by indicating that the full company name “Hangzhou Datou & You Technology Co., Ltd.” should be used as the filter condition.
How to use this feature:
-
Default Settings:
The system automatically enables the AI Search Index for certain fields. By default, it is enabled for short text fields of string type, excluding long text, date, numeric, or other data types. These fields help the AI more accurately match user queries. -
Manual Configuration:
If you want to enable or disable the search feature for other fields, you can use the toggle switch. Simply click the switch next to the field you want to adjust and choose to enable or disable it.
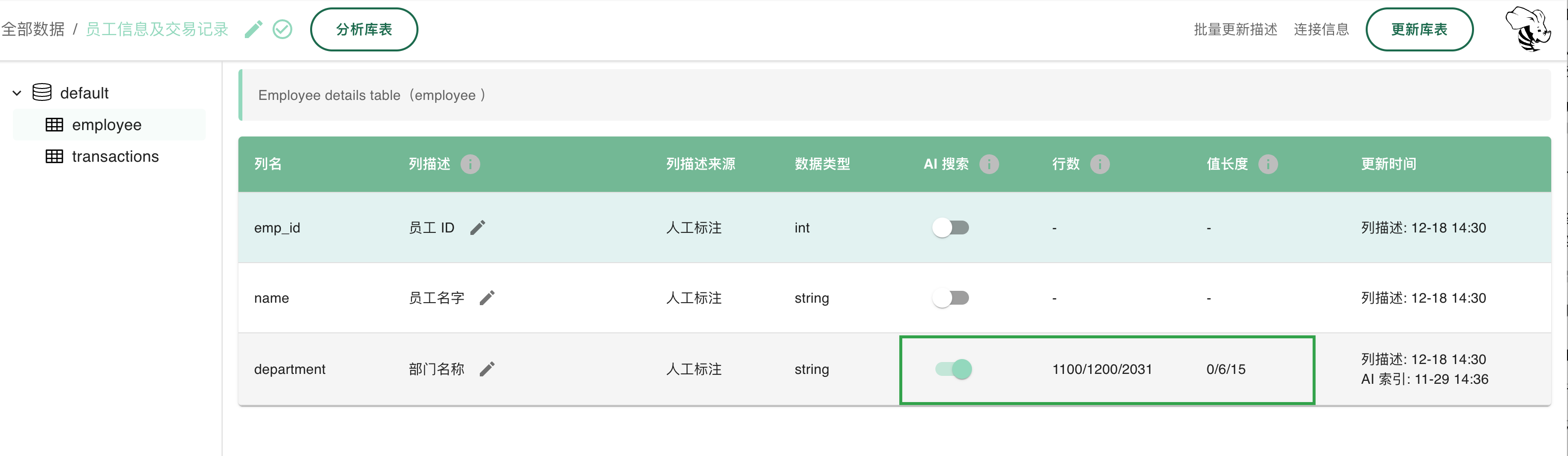
Why do we need a toggle button?
In some cases, enabling too many indexes can affect system performance because each index consumes computing resources. Therefore, we provide a toggle switch, allowing you to enable or disable certain fields’ indexes as needed to balance performance and accuracy.
-
Enable AI Search:
The AI will be more intelligent in understanding and matching your questions, improving query accuracy. -
Disable AI Search:
Potentially improves system performance but may reduce the accuracy of some queries.
What is the difference between AI Search and Terminology (Synonyms)?
Both can be used to improve query accuracy, but they apply to different scenarios:
-
AI Search (Fuzzy Search):
AI Search identifies similar queries through fuzzy matching. It’s suitable for keywords that explicitly exist in your database—such as company names or product names—that users might refer to in abbreviated or alternative forms. If there are thousands or even tens of thousands of these keywords, AI Search is recommended to avoid manual synonym configuration. -
Add Terminology (Synonyms):
This is used to handle business terms that do not directly appear in your database but may appear in user questions. AskTable needs to understand these terms to correctly interpret user intent and business context. For example, if “iron box” is set as a synonym for “engine,” AskTable will not mistakenly search for literal iron boxes. This feature can also be used for custom or organization-specific vocabulary, including certain business metrics.
Summary:
-
Enabled by default:
For most scenarios, the system automatically enables AI Search for certain fields. -
User Configuration:
You can manually enable or disable AI Search for particular fields, providing flexibility to meet various needs. -
Optimize Performance:
Too many indexes can affect system performance, so it’s recommended to enable only those necessary.
By configuring the AI Search feature, you can increase the flexibility and accuracy of AI queries, while also optimizing system performance based on your needs.
User Considerations:
- Enabling AI Search may increase the system’s computational load, so only enable it when necessary.
- The default enabled fields have been optimized for most user scenarios.